Tesla’s Robotaxi Launch in Austin Faces Regulatory Scrutiny After Incidents
Tesla’s much-anticipated pilot robotaxi service in Austin, Texas, has quickly attracted the attention of federal safety regulators following social media videos depicting erratic driving behavior. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) confirmed on Monday it has contacted Tesla to gather more information after the clips showing incidents surfaced online.
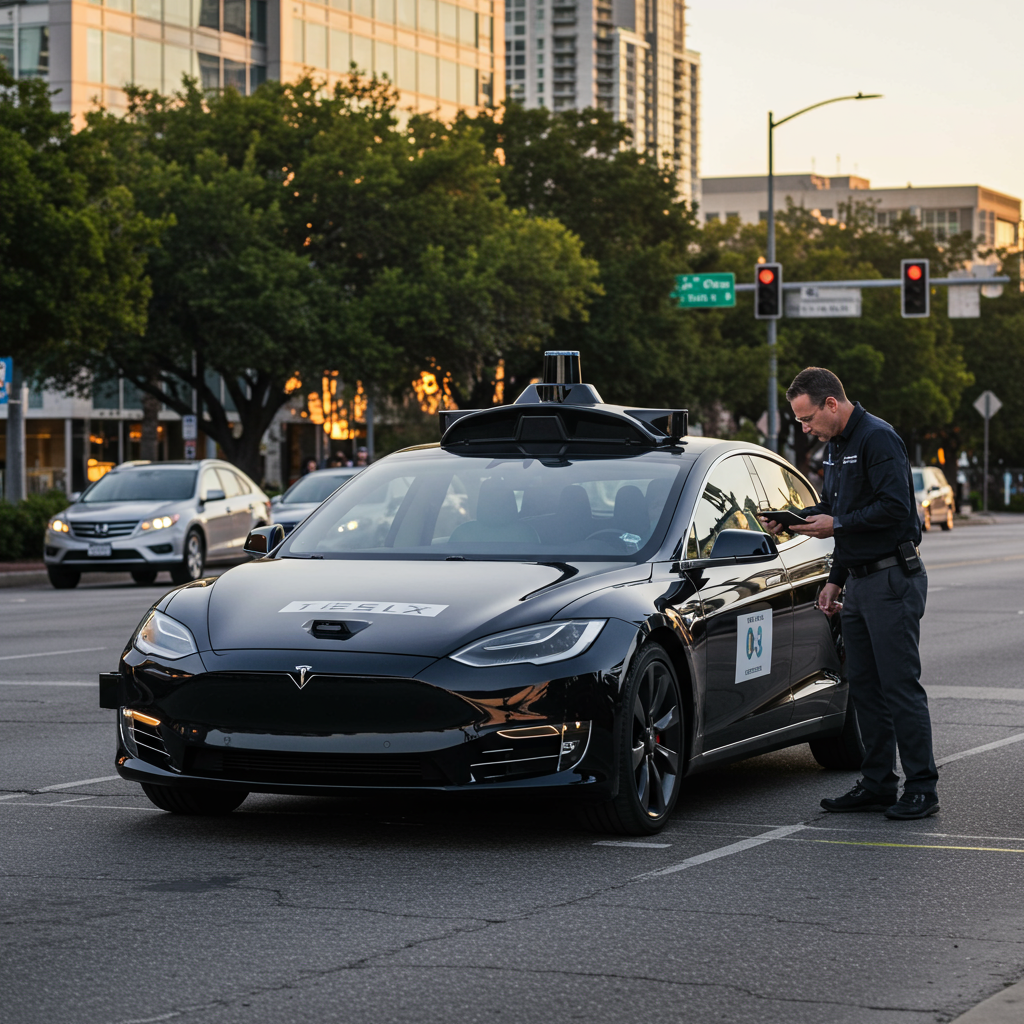
The autonomous ride-hailing service made its debut in Austin on Sunday, initially available on an invitation-only basis to a select group of users, primarily individuals known for promoting Tesla and its CEO, Elon Musk.
Videos widely shared online reportedly showed concerning maneuvers by the Tesla robotaxis. Examples cited include one vehicle traveling the wrong way on a street and another braking abruptly in traffic, apparently reacting to stationary police vehicles positioned outside its intended path.
A NHTSA spokesperson stated the agency “is aware of the referenced incidents and is in contact with the manufacturer.” Tesla Vice President of Vehicle Engineering Lars Moravy and regulatory counsel Casey Blaine did not immediately respond to requests for comment regarding the incidents or the agency’s contact.
Limited Pilot Program Amidst Broader Safety Concerns
This Austin launch represents a limited pilot program, utilizing fewer than two dozen modified Tesla Model Y SUVs. These vehicles are equipped with the company’s latest “FSD Unsupervised” software and hardware. The service operates under specific constraints: it’s limited to daylight hours, requires good weather conditions, and importantly, includes a human safety supervisor seated in the front passenger seat during trips. Invited users participate under terms of an “early access program,” restricted to a specific geofenced area within the city and excluding trips like those to airports. Remote operators are also reportedly monitoring the vehicles.
While Musk has recently indicated plans to expand robotaxi services to Los Angeles and San Francisco after the Austin pilot, the rollout faces significant hurdles beyond these initial incidents. Texas lawmakers had previously called for Tesla to delay its Austin launch until September 1, when new state self-driving laws take effect, citing public safety concerns and seeking clarity on Tesla’s compliance plans.
Safety advocates have also voiced strong criticisms regarding Tesla’s autonomous capabilities. Organizations like The Dawn Project have demonstrated instances where Tesla’s current “Full Self Driving” (FSD) software allegedly failed to recognize hazards like a stopped school bus or a child-sized mannequin, arguing the technology is not yet ready for widespread deployment. NHTSA’s existing investigation into potential safety defects with Tesla’s FSD-Supervised (previously FSD Beta) systems, initiated after accidents resulting in injuries and fatalities, remains ongoing.
Past Promises and the Competitive Landscape
The federal safety regulator’s standard practice is not to “pre-approve new technologies or vehicle systems.” Instead, automakers self-certify that their vehicles meet federal safety standards. NHTSA investigates “incidents involving potential safety defects” and takes action as needed after reviewing reports and information.
The Austin debut occurs amidst a history of ambitious, yet often missed, deadlines set by Elon Musk for Tesla’s autonomous driving and robotaxi capabilities. As far back as 2015, Musk predicted “full autonomy” within three years. In 2019, he was “very confident” Tesla would have one million robotaxi-ready vehicles operational by 2020.
Meanwhile, competitors have been advancing. Alphabet’s Waymo, for instance, recently announced surpassing 10 million paid autonomous trips. Companies in China, including Baidu’s Apollo Go, WeRide, and Pony.ai, are also operating commercial robotaxi fleets, positioning them ahead in terms of real-world operational experience.
Although the Austin launch contributed to an uptick in Tesla’s stock price on Monday, its limited scope and the swift emergence of safety concerns and regulatory attention highlight the significant challenges remaining in achieving fully autonomous, commercially viable ride-hailing services.