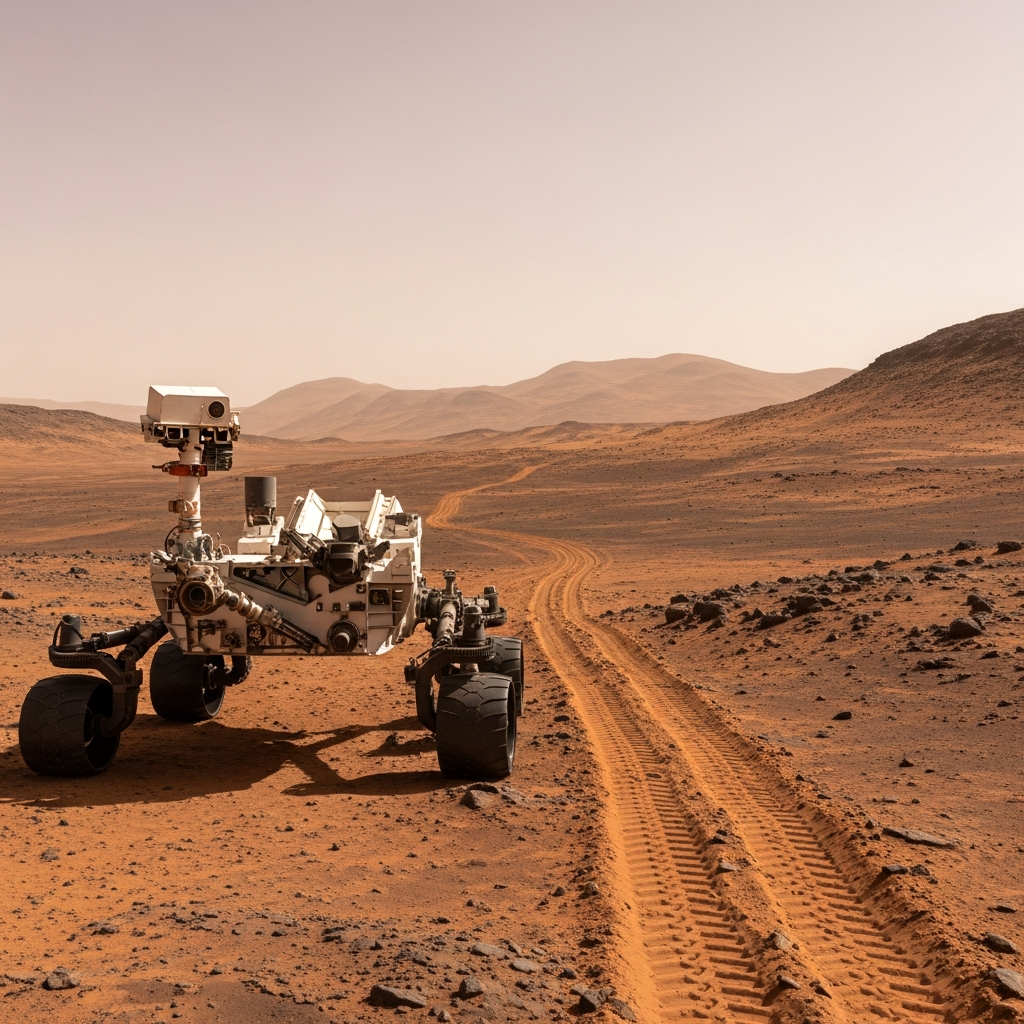
NASA’s Perseverance rover has achieved a monumental milestone on the Red Planet, officially traversing the equivalent distance of a full marathon – an incredible 42.2 kilometers (26.3 miles). This groundbreaking accomplishment highlights the rover’s remarkable endurance and sophisticated engineering, marking a new chapter in robotic Mars exploration. Beyond this impressive feat, Perseverance is now poised to break another significant record, aiming to become the longest-distance traveler on another celestial body, a title currently held by its predecessor, the Opportunity rover.
For nearly five years, Perseverance has meticulously explored the ancient river delta within Jezero Crater, diligently searching for signs of past microbial life. Its mission extends beyond geological surveys; it’s about understanding Mars’s history and setting the stage for future human missions. This article delves into the rover’s incredible journey, its record-breaking movements, and the cutting-edge technology propelling it forward.
The Martian Marathon: Perseverance’s Historic Journey
Just before its five-year anniversary, the Perseverance rover officially completed its Martian marathon. This feat underscores the robust design and operational excellence of NASA’s robotic explorer. While the original article noted Perseverance was nearing a marathon, recent updates confirm it has now surpassed the 42.2-kilometer mark. This isn’t just about distance; it’s a testament to sustained performance in an incredibly harsh, alien environment.
The rover’s journey has not been without its challenges. From navigating treacherous terrain to enduring communication blackouts when Mars is behind the Sun, every kilometer represents a triumph of engineering and mission planning. Yet, Perseverance continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible, providing unprecedented insights into the Red Planet.
Five Years of Unprecedented Exploration
Since its landing in February 2021, Perseverance has been a scientific powerhouse. Its primary goal is to study the geology of Jezero Crater, a site believed to have once harbored a vast lake and river delta. This ancient watery environment makes it a prime location to seek biosignatures – potential evidence of ancient microbial life. The rover has already identified what scientists consider the most promising rock sample to date, hinting at Mars’s potentially habitable past. These invaluable rock core samples are being cached for the future Mars Sample Return mission, an ambitious endeavor to bring Martian materials back to Earth for in-depth analysis.
Beyond the Marathon: Chasing Opportunity’s Legacy
Having conquered the marathon, Perseverance now sets its sights on an even grander record: the longest distance ever driven on another world. That title currently belongs to NASA’s Opportunity Mars rover, which traversed an astounding 45.16 kilometers (28.06 miles) during its nearly 15-year mission. Perseverance is on track to surpass this within months, and at a significantly faster pace.
Mark Maimone, a long-time rover driver and mobility engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), highlighted this remarkable speed. “Opportunity drove for nearly 15 years, whereas we are not yet at five years of operations, so we’re likely to surpass Opportunity’s record 3x faster than it did!” he explained. This rapid progress allows the science team to explore more diverse geological features, such as ancient river delta formations and mineral-rich zones, which are crucial for finding clues about past microbial life.
The Autonomous Advantage: How Perseverance Drives Itself
The secret to Perseverance’s swift and extensive travels lies in its groundbreaking autonomous driving capabilities. Unlike its predecessors, Perseverance is equipped with sophisticated AI-powered software that enables it to navigate vast distances with minimal human intervention. Over 90% of its journey has been conducted autonomously, a pivotal advancement for deep space exploration.
On June 19, 2025 (Sol 1540), Perseverance set a record for its longest single drive, covering an impressive 411.7 meters (1,350.7 feet) in approximately 4 hours and 24 minutes. This feat was made possible by its Enhanced Autonomous Navigation (ENav) system. ENav utilizes primitive neural networks and convolutional neural networks to analyze images from the rover’s cameras in real-time. This allows it to distinguish safe, solid rock from treacherous sand dunes and other hazards up to 15 meters (50 feet) ahead, evaluating terrain for each of its six wheels independently. This level of self-driving intelligence drastically reduces the need for frequent pauses to consult with Earth-based teams, saving weeks of mission time, especially when traversing complex boulder fields.
Engineering Marvel: Powering Future Mars Missions
Perseverance is a masterpiece of engineering designed for durability and extended operation. Rigorous system checks conducted by engineers at JPL confirm the rover’s excellent condition. Its robust hardware, including rotary wheel actuators, is certified for at least another 60 kilometers (37 miles) of driving, with a projected total capability of 100 kilometers (61 miles) over its lifespan. This remarkable longevity serves as a blueprint for future interplanetary missions.
NASA has expertly applied lessons learned from earlier missions to ensure Perseverance’s sustained health. Past rovers like Spirit and Opportunity faced critical issues, such as a lost drive motor or an extended arm due to mechanical failure, yet they continued to operate, making significant discoveries. Curiosity had to completely redevelop its drilling strategy after a motor failed. Each instance taught engineers how to adapt operational strategies and extend mission lifespans. This accumulated knowledge underpins Perseverance’s ability to “persevere” through potential future challenges, ensuring its scientific contributions continue for years to come.
Built to Last: Overcoming Martian Challenges
Operating a rover on Mars presents a myriad of challenges: extreme temperature fluctuations, abrasive dust, and significant communication delays of up to 20 minutes one-way. Despite these hurdles, Perseverance’s hardware has shown minimal wear, navigating rocky terrain with incredible resilience. The human rover planners meticulously chart the safest and most efficient routes using satellite images for longer drives, while the rover’s autonomous navigation performs dozens of checks per second to guarantee its safety. This blend of human expertise and robotic autonomy is crucial for maximizing exploration efficiency and ensuring mission success.
A Dream Come True: The Human Element of Mars Exploration
Behind every robotic triumph on Mars are the dedicated individuals on Earth. Mark Maimone perfectly captures the awe and wonder of their work: “The prospect of being one of the first humans to see pictures from another world filled me with awe. Yet every time we drive to a new location, that’s exactly what our rover planners get to do; driving on Mars is truly a dream come true.” This profound connection to discovery fuels the relentless pursuit of knowledge about our solar system. The collaboration between human ingenuity and advanced AI is not only propelling Perseverance across Mars but also inspiring a new generation of scientists and engineers.
Frequently Asked Questions
How far has NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover traveled, and what major records has it achieved?
As of recent updates, NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover has officially traveled over 42.2 kilometers (26.3 miles) on the Red Planet, successfully completing the equivalent distance of a full marathon. This accomplishment marks a significant milestone in its mission. Additionally, Perseverance set a record for its longest single drive on June 19, 2025 (Sol 1540), covering 411.7 meters (1,350.7 feet). It is now on track to surpass the 45.16-kilometer (28.06 miles) record set by the Opportunity rover, potentially becoming the longest-distance traveler on another world at a significantly faster pace.
What is autonomous driving, and how does it help Perseverance navigate Mars?
Autonomous driving refers to the Perseverance rover’s advanced capability to navigate the Martian surface with minimal human intervention, relying on its onboard AI systems. This is achieved through its Enhanced Autonomous Navigation (ENav) system, which uses primitive neural networks to analyze camera images in real-time. ENav can detect hazards up to 15 meters (50 feet) ahead, differentiate between safe rocks and treacherous sand, and independently evaluate terrain for each wheel. This allows Perseverance to make real-time decisions, reducing the need for constant communication with Earth and enabling it to cover over 90% of its distance autonomously, drastically saving mission time.
What are the long-term prospects for the Perseverance mission, and what future discoveries can we expect?
The long-term prospects for the Perseverance mission are robust. Engineers at NASA’s JPL have certified the rover’s rotary wheel actuators for at least another 60 kilometers (37 miles) of driving, suggesting a total operational capability of 100 kilometers (61 miles). The rover’s mission is expected to continue well beyond its five-year anniversary in February 2026. Future discoveries will likely involve continued exploration of Jezero Crater’s diverse geological features, including ancient river delta formations. The rover will continue collecting rock core samples for the Mars Sample Return mission, which aims to bring these precious materials back to Earth for in-depth analysis, providing unparalleled insights into Mars’s past habitability and potential for ancient life.
Conclusion
The Perseverance rover stands as a beacon of scientific and engineering prowess, pushing the boundaries of interplanetary exploration. Its completion of a Martian marathon, coupled with its groundbreaking autonomous driving technology, has fundamentally reshaped our understanding of what robotic explorers can achieve. As it continues its journey, chasing new distance records and uncovering the Red Planet’s ancient secrets, Perseverance is not just collecting samples or charting new paths; it is paving the way for humanity’s eventual arrival on Mars, proving that with ingenuity and perseverance, dreams truly can come true on another world.