A senior Kremlin official was reportedly told by a Trump envoy that Ukraine must cede territory as a condition for a peace agreement. This bombshell revelation, emerging from a private phone call, has cast a significant shadow over international efforts to resolve the nearly four-year-long conflict. It also appears to be the genesis of a controversial 28-point peace proposal, sparking widespread debate and alarm among Ukraine’s allies. This article dives deep into the alleged discussions, the plan’s contentious details, and the global reactions to its far-reaching implications.
The Alleged Phone Call & Initial Overtures
In a significant development reported by Bloomberg, Donald Trump’s special envoy, Steve Witkoff, allegedly communicated directly with Yuri Ushakov, a top foreign policy advisor to Russian President Vladimir Putin. During a private phone call on October 14, Witkoff reportedly outlined that a lasting peace deal in Ukraine would necessitate Russia securing control of the Donetsk region. He also suggested the potential for other territorial exchanges. A transcript of the five-minute conversation reportedly captured Witkoff stating, “Now, me to you, I know what it’s going to take to get a peace deal done: Donetsk and maybe a land swap somewhere.”
Witkoff, who previously played a role in brokering a Gaza ceasefire agreement, reportedly advised Ushakov to adopt a more optimistic tone in discussions and to praise Trump. He suggested modeling a joint peace framework on the successful Gaza deal, proposing a “20-point Trump plan for peace.” The envoy also offered tactical guidance for Putin, including scheduling a phone call with Trump before Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy‘s planned White House visit. Ushakov seemingly took some of this advice, indicating Putin would congratulate Trump as “a real peace man.” This exchange provides direct insight into the diplomatic strategy guiding the proposed settlement.
Unpacking the Controversial 28-Point Peace Proposal
The reported phone call appears to be the precursor to a contentious 28-point peace proposal that surfaced in November. This draft plan, widely characterized as highly favorable to Russia, details extensive concessions from Ukraine and significant benefits for Moscow. It has drawn sharp criticism for potentially rewarding aggression and undermining international norms.
Here are the key provisions reportedly outlined in the Trump Ukraine peace plan:
Extensive Territorial Demands
Ukraine would be required to cede control of Crimea, Luhansk, and Donetsk in their entirety to Russia. This includes areas currently under Ukrainian control within Donetsk. The proposal also suggests freezing current battle lines in Kherson and Zaporizhzhia, effectively recognizing Russian occupation of those parts. A demilitarized buffer zone would be established in the withdrawn Donetsk territories, internationally recognized as Russian Federation land. Russia would, in turn, relinquish other agreed territories it controls outside these five regions.
Severe Military Limitations & NATO Exclusion
Kyiv’s armed forces would face substantial reductions, shrinking from approximately 880,000 troops to around 600,000. The plan would also prohibit Ukraine from joining NATO, amending the alliance’s statutes to prevent future Ukrainian membership and forbidding the stationing of NATO troops on Ukrainian soil. This addresses a long-standing demand from Moscow.
Economic Reintegration for Russia
In exchange for these concessions, Russia could see a gradual lifting of international sanctions and reintegration into the global economy, potentially including an invitation to rejoin the G8. The plan also envisions long-term economic cooperation agreements between the US and Russia across various sectors.
Financial Aid and Asset Repurposing
An estimated $100 billion in frozen Russian assets from the US, plus an additional $100 billion from Europe, would be dedicated to Ukraine’s reconstruction. The US would reportedly receive 50% of the profits from its share of the reconstruction venture. Ukraine would also be eligible for EU membership and receive short-term preferential access to the European market.
Conditional Security Guarantees for Ukraine
Ukraine would receive “reliable security guarantees.” However, these guarantees come with significant caveats. A future “significant, deliberate and sustained armed attack” by Russia would be deemed “threatening the peace and security of the transatlantic community,” but this would not obligate military intervention from the US or European allies. Specific conditions for revocation of the US guarantee include Ukraine invading Russia or launching unprovoked missile attacks.
Political and Humanitarian Measures
The plan calls for elections in Ukraine within 100 days, enshrined non-nuclear status for Ukraine, and mutual educational programs promoting understanding. It mandates the abolition of discriminatory measures, guarantees media and education rights for both Ukrainian and Russian languages, and prohibits “Nazi ideology and activities.” Humanitarian aspects include an “all for all” prisoner exchange, return of civilian detainees and hostages (including children), and a family reunification program.
Shared Infrastructure Control
The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, captured early in the conflict, would operate under IAEA supervision, with its electricity distributed equally between Russia and Ukraine (50:50). Ukraine’s gas infrastructure would be rebuilt and operated jointly with US cooperation. Agreements would also ensure Ukraine’s commercial use of the Dnieper River and free transport of grain across the Black Sea.
Amnesty and Enforcement
All parties involved in the conflict would receive full amnesty for wartime actions. The agreement would be legally binding, monitored, and guaranteed by a “Peace Council” headed by Donald J. Trump, with sanctions for violations. A ceasefire would take effect immediately upon agreement.
Global Reactions and Geopolitical Fallout
The leak of this detailed proposal has ignited a firestorm of international debate, revealing stark divisions and deeply entrenched “red lines.”
Ukraine’s Adamant Stance
While Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy adopted a cautiously diplomatic tone, expressing readiness for “constructive, honest and prompt work” on the “draft plan” with the White House, other senior Ukrainian officials have vehemently rejected its core tenets. Rustem Umerov, a top advisor, reportedly agreed to most of the plan after modifications, but Ukraine’s deputy U.N. Ambassador Khrystyna Hayovyshyn stated unequivocally that Ukraine would never recognize Russian-occupied territory as Russian. She emphasized that Ukraine would not accept limits on its right to self-defense, the size of its armed forces, or its sovereign right to choose alliances. Ukrainian MP Kira Rudik noted the plan’s timing coincided with pressure on Zelenskyy amid a corruption scandal. Ukraine’s constitution also explicitly prohibits territorial concessions.
European Allies Express Alarm
European diplomats were reportedly “blindsided” by the revelations, insisting that both Ukraine and European nations must be central to any peace process. EU foreign policy chief Kaja Kallas stressed, “For any plan to work, it needs Ukrainians and Europeans on board.” She critically questioned the lack of concessions from the Russian side and warned against “rewarding aggression.” German Foreign Minister Johannes Wadephul and French Foreign Minister Jean-Noel Barret echoed these sentiments, asserting that peace cannot equate to Ukrainian “capitulation.” There is a strong consensus among European leaders against any agreement that could be perceived as emboldening Russian President Vladimir Putin’s aggression.
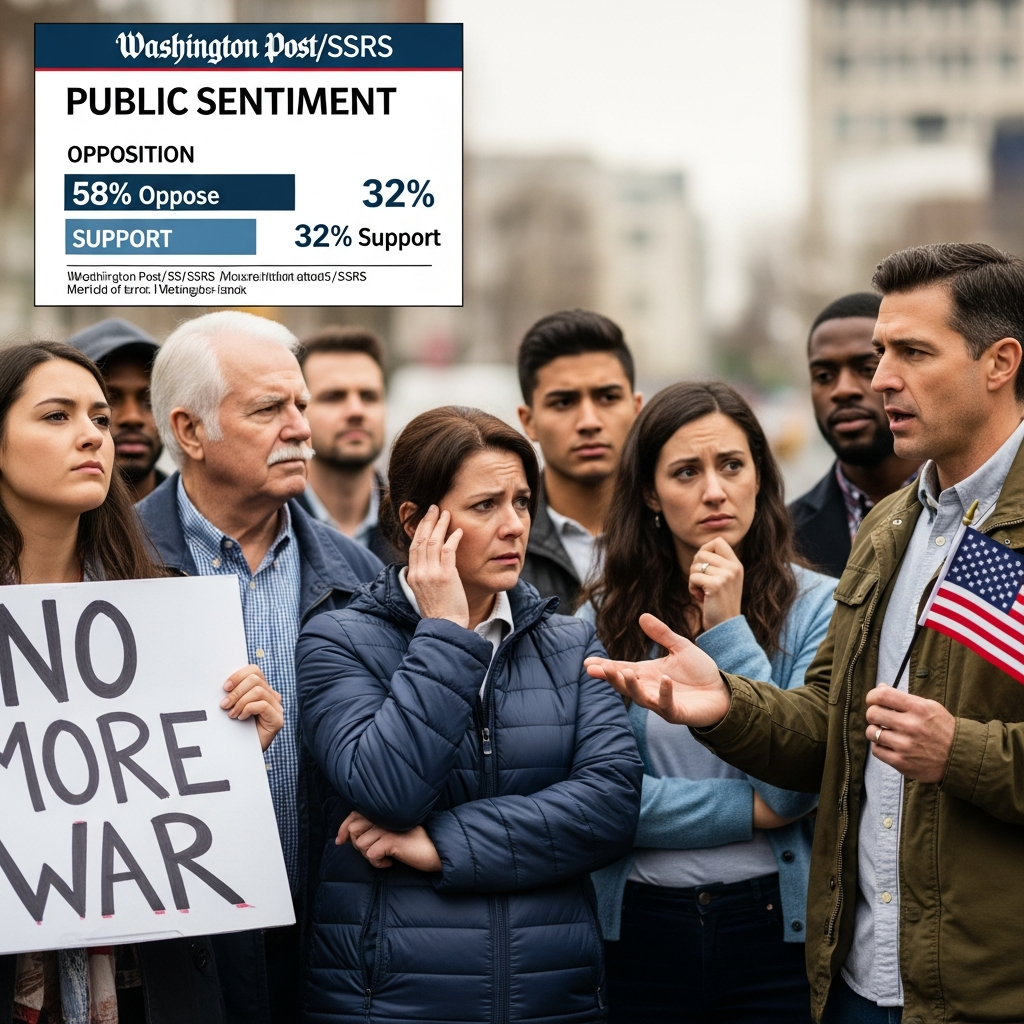
US Internal Views and Divergent Perspectives
Within the US, the plan has also generated mixed reactions. Secretary of State Marco Rubio reportedly played a role in developing the plan, stating that “difficult but necessary concessions” would be required from both sides for a durable peace. However, U.S. Rep. Don Bacon, an Air Force veteran, vehemently rejected the plan as “Unacceptable,” drawing comparisons to the “1938 Munich” agreement, widely regarded as a catastrophic act of appeasement. White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt confirmed Trump’s frustration with both sides’ unwillingness to commit to an agreement. Interestingly, the phone conversation between Witkoff and Ushakov occurred on the same day Trump publicly voiced frustration with Putin’s unwillingness to end the war, questioning why he “continues with this war.”
Context and Complications: A Tapestry of Diplomacy and Conflict
The emergence of this controversial proposal comes amidst a complex backdrop of ongoing conflict, internal Ukrainian political challenges, and shifting international diplomacy.
Diplomatic Maneuvers and Battlefield Realities
Trump’s announcement of dispatching Witkoff to meet Putin in Moscow and US Army Secretary Dan Driscoll to meet with Ukrainians—ahead of a potential White House meeting with Zelenskyy—underscores the high-stakes diplomatic flurry. Trump stated on Truth Social that he would meet with leaders “ONLY when the deal to end this War is FINAL or, in its final stages.” However, the US has reportedly pushed Ukraine to accept such a framework as a foundation for ending the nearly four-year conflict.
Meanwhile, the war on the ground continues. While Russian army commanders claimed the capture of key hubs like Kupiansk and significant control in Pokrovsk, the Ukrainian military has denied these claims. The humanitarian situation remains dire, with millions displaced and critical infrastructure targeted.
Ukraine’s Internal Challenges: The Corruption Scandal
Adding another layer of complexity, Ukraine is grappling with a significant internal challenge: the “Operation Midas” corruption scandal. This alleged $100 million kickback scheme within the state-owned nuclear power company, Energoatom, has led to high-profile dismissals and criticisms. There are reports suggesting that Trump might leverage American influence to halt corruption investigations against Zelenskyy and his associates if Kyiv accepts the peace plan. This internal pressure could significantly influence Ukraine’s negotiating position and public opinion regarding any peace proposals.
Analyzing the Broader Implications
This alleged Trump Ukraine peace plan represents a profound potential shift in international diplomacy and a challenge to post-World War II principles of territorial integrity. If implemented, it would largely legitimize Russia’s territorial gains through military aggression, setting a dangerous precedent for future conflicts. The severe limitations on Ukraine’s sovereignty, military capabilities, and alliance choices could fundamentally alter the geopolitical landscape of Eastern Europe.
The plan highlights a deep divergence between Trump’s “deal-making” approach and the steadfast commitment of Ukraine and its European allies to international law and the deterrence of further aggression. The significant hurdles—Ukraine’s constitutional prohibitions, the widespread European opposition, and the fundamental question of whether rewarding an aggressor leads to genuine, lasting peace—suggest that while diplomatic efforts may intensify, a universally acceptable resolution remains profoundly elusive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main points of Donald Trump’s alleged 28-point peace plan for Ukraine?
The controversial 28-point peace plan, reportedly stemming from discussions between Trump envoy Steve Witkoff and a Kremlin official, proposes significant concessions from Ukraine. Key provisions include Ukraine ceding the entirety of Crimea, Luhansk, and Donetsk to Russia, along with freezing current battle lines in Kherson and Zaporizhzhia. Ukraine’s military would be drastically reduced, and it would be constitutionally barred from joining NATO. In return, Russia could see sanctions lifted and reintegrated into the G8. The plan also suggests using $200 billion in frozen Russian assets for Ukraine’s reconstruction, with specific, conditional security guarantees for Kyiv.
How have Ukraine and European allies reacted to the proposed peace plan?
Reactions to the plan have been largely critical, particularly from Ukraine and its European allies. While Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy expressed readiness for “constructive work” on the draft, other senior Ukrainian officials vehemently reject territorial concessions, citing constitutional prohibitions and national sovereignty. European diplomats, reportedly “blindsided,” have voiced strong opposition to any agreement that could be perceived as rewarding Russian aggression, insisting that both Ukraine and European nations must be fully involved in any peace process. Many European leaders view the plan as potentially undermining international law and emboldening future aggressors.
What are the key obstacles preventing this peace plan from being accepted?
Numerous significant obstacles impede the acceptance of this peace plan. Foremost is Ukraine’s unwavering insistence on territorial integrity and its constitutional prohibition against ceding land to an aggressor. European allies staunchly oppose any deal that appears to legitimize Russia’s military gains, fearing it would set a dangerous global precedent. Furthermore, the plan’s limitations on Ukraine’s military and its exclusion from NATO are seen as compromising its sovereignty and future security. The conditional and arguably weak security guarantees offered to Ukraine, coupled with Russia’s lack of substantive concessions, also present major sticking points, making genuine, lasting peace difficult to achieve.
Conclusion
The alleged “Trump Ukraine peace plan,” with its far-reaching stipulations and the diplomatic storm it has unleashed, underscores the profound complexities inherent in resolving the protracted conflict. Rooted in reported private discussions between a Trump envoy and a senior Kremlin official, the detailed 28-point proposal calls for significant Ukrainian territorial concessions, military reductions, and a reorientation of its geopolitical alignment. While framed as a pathway to peace, the plan faces formidable opposition from Ukraine, which steadfastly rejects ceding sovereign land, and from European allies, who fear rewarding aggression. As diplomatic efforts intensify and the conflict grinds on, the viability of such a contentious framework remains deeply uncertain, highlighting the ongoing tension between pragmatic deal-making and the bedrock principles of international law.