US Inflation Stays Subdued, Defying Expectations for Fourth Consecutive Month
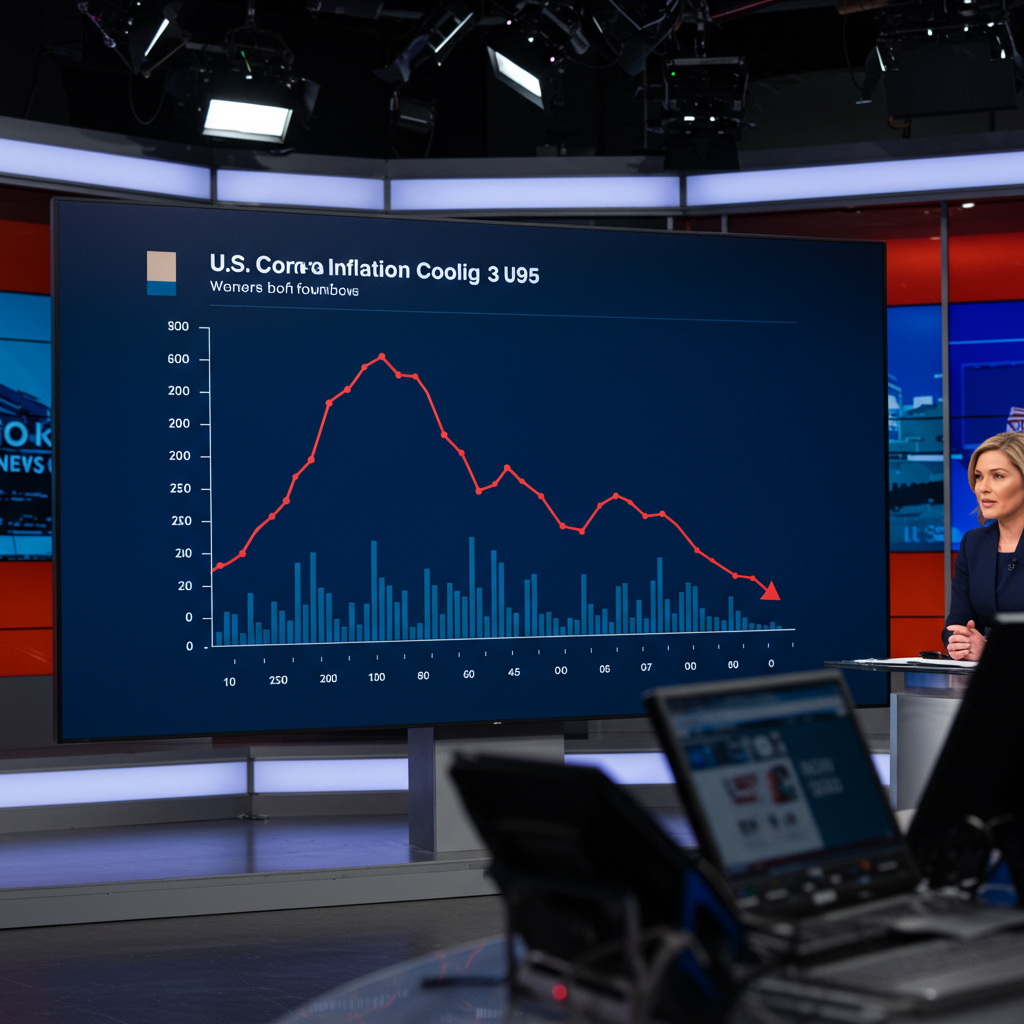
Latest data released by the US government shows that inflation continues to cool more than anticipated, marking the fourth consecutive month that key price measures have come in below economist forecasts. This sustained trend is offering reassurance to policymakers and investors alike, particularly against a backdrop where some had feared that trade policies could reignite price pressures.
The consumer price index (CPI), stripping out the often-volatile costs of food and energy to provide a clearer view of underlying inflation trends, increased by a modest 0.1% from the previous month. This figure underscores the persistent easing of inflationary pressures seen since late last year. The overall headline CPI for May also remained moderate, rising 2.4% annually.
A Consistent Pattern of Cooling Prices
This isn’t a one-off event. The latest figures extend a pattern of inflation pressures easing more rapidly than projected. Data from December 2024 already showed a significant slowdown in core CPI, marking the first monthly rate drop in six months and reaching 3.2% year-over-year. A subsequent report covering January 2025 inflation was also described as “benign,” further cementing the view that the disinflationary trend was taking hold.
Many economic forecasts had predicted a potential uptick in inflation, partly attributing this risk to the possible impact of trade policies, such as tariffs. However, the data has consistently defied these expectations, suggesting that factors like the holding of some threatened levies or other disinflationary forces are currently dominant.
Implications for the Federal Reserve and Markets
The persistent trend of cooler-than-expected core inflation carries significant weight for the Federal Reserve and its monetary policy decisions. It eases the pressure on the central bank to consider further interest rate hikes and reinforces the growing market expectation that the Fed will be able to cut rates later in 2025.
Previous inflation reports that showed unexpected cooling, such as those in December and January, were met with broadly positive reactions in financial markets, fueling rallies in both stocks and bonds as investors increased bets on forthcoming rate cuts. The latest CPI data further supports the narrative that the Fed has room to be patient and potentially adjust rates downward without jeopardizing its goal of price stability. Earlier economic data from mid-2024 already indicated inflation metrics preferred by the Fed were easing, setting an initial stage for potential rate adjustments.
Mixed Signals Amidst the Trend
While the overall picture painted by the core CPI is one of easing pressures, the landscape isn’t uniform. Some areas have seen price increases, such as groceries, which rose 0.3% in May after a decline in April. Retailers and car manufacturers have also voiced warnings about potential price hikes. Furthermore, some regional surveys conducted by the Federal Reserve indicate that businesses in certain parts of the country still anticipate “strong” future price increases.
Despite these mixed signals, the continued moderation in core inflation provides a strong indicator that overall price pressures are moving in the right direction, supporting the economic resilience shown by solid growth figures earlier in the year and keeping the focus on the timing of potential shifts in interest rate policy.