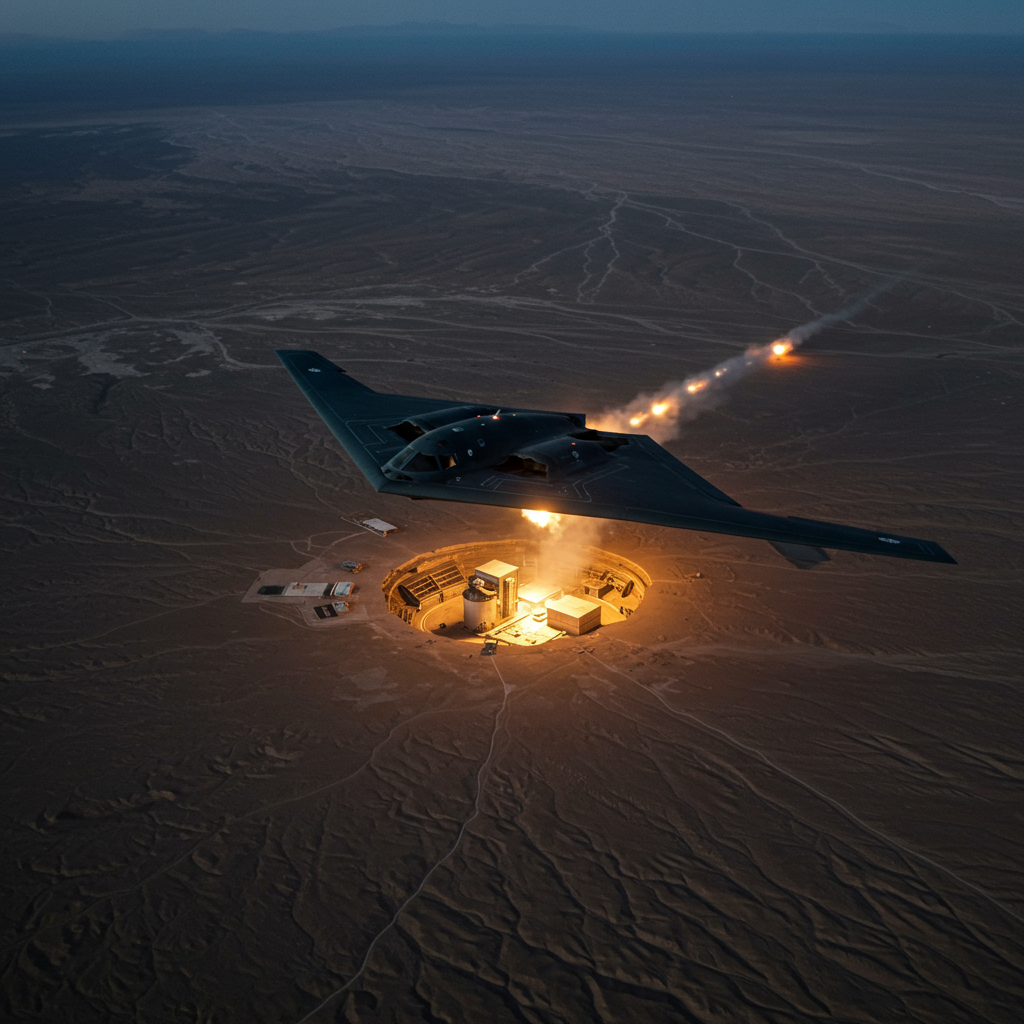
It was a military operation years in the making, executed with a level of secrecy and deception rarely seen. On June 22, 2025, the United States launched a massive, precision strike against key underground nuclear enrichment facilities in Iran, reportedly achieving complete surprise. Codenamed Operation Midnight Hammer, the mission utilized a combination of B-2 Spirit stealth bombers and submarine-launched cruise missiles in what U.S. officials hailed as a devastating blow to Iran’s nuclear program.
The operation unfolded amidst a broader, escalating conflict between Israel and Iran, with Israeli forces having conducted strikes against Iranian military and air defense capabilities for over a week prior. The U.S. action marked a significant escalation, directly targeting sites critical to Iran’s nuclear ambitions.
The Mission: Objectives and Claims
According to U.S. officials, the primary objective of Operation Midnight Hammer was the “destruction of Iran’s nuclear enrichment capacity” and to halt the perceived threat posed by its nuclear program. The White House claimed Iran was mere days away from potentially obtaining a nuclear bomb, framing the strike as necessary preventative action.
Following the attack, U.S. leaders were quick to declare success. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth asserted that “Iran’s nuclear ambitions have been obliterated,” while President Donald Trump described the strikes as a “spectacular military success,” claiming key facilities were “completely and totally obliterated.” However, Iran vehemently denied that significant damage had occurred and swiftly pledged retaliation, condemning the U.S. action as a violation of international law.
Operation Midnight Hammer: A Masterclass in Stealth and Deception
Key to the operation’s success was a sophisticated multi-layered strategy designed to maintain tactical surprise.
- Public Misdirection: Days before the attack, President Trump publicly announced he would delay a decision on striking Iran for two weeks, ostensibly to allow for negotiation. U.S. officials later confirmed this was a deliberate ruse to mask the impending operation.
- Decoy Flight Path: As the mission commenced, a group of B-2 stealth bombers departed Whiteman Air Force Base in Missouri and flew west towards the Pacific, attracting public and media attention. Simultaneously, the main strike force of seven B-2s took off and flew east, maintaining strict radio silence to avoid detection.
- Furtive Long-Haul Flight: The seven strike bombers undertook an arduous 18-hour flight eastward, requiring multiple aerial refuelings to reach the Middle East. This long-range capability is a hallmark of the B-2, which can project U.S. airpower globally from its Missouri base.
According to U.S. officials, this elaborate deception plan, combined with the B-2’s inherent stealth capabilities, allowed the bombers to arrive in the Eastern Mediterranean undetected by Iranian forces. The B-2s were reportedly escorted by other stealthy U.S. fighter and reconnaissance aircraft before entering Iranian airspace.
Striking Deep Underground with “Bunker Busters”
The core of the U.S. attack relied on highly specialized munitions designed to penetrate deeply buried and hardened targets – the Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP), or GBU-57 bomb.
Targets: The primary targets were Iran’s underground uranium enrichment plants at Fordo and Natanz. Another site in Isfahan, involved in uranium preparation, was also targeted.
Munitions: The seven B-2 bombers each carried two GBU-57 bombs. These massive, 30,000-pound weapons are designed to burrow up to 200 feet underground before detonating. Operation Midnight Hammer marked the first operational use of the GBU-57 in combat.
Multifaceted Attack: Approximately an hour before the B-2s reached their targets, a U.S. submarine in the region launched over two dozen Tomahawk cruise missiles towards sites, including the one in Isfahan. These missiles struck their targets shortly after the B-2s began their bombing runs, potentially adding a layer of confusion or serving as a preliminary strike.
U.S. officials stated that Iran’s military appeared completely unaware of the inbound aircraft. No Iranian fighter jets were scrambled, nor were surface-to-air missiles fired at the stealthy American jets during the attack, which lasted about half an hour as bombs and missiles found their marks.
The Scale of the Operation
Operation Midnight Hammer was one of the largest and most complex B-2 missions ever conducted:
Aircraft: Over 125 aircraft were involved in total, including the B-2 strike and decoy bombers, numerous refueling tankers, fighter escorts, and intelligence/surveillance drones.
Precision Weapons: 75 precision-guided weapons were used, including 14 GBU-57 “bunker buster” bombs and over two dozen Tomahawk cruise missiles. The B-2s delivered a total of 420,000 pounds of explosives.
Historic Significance: U.S. military leaders noted this was the largest B-2 operational strike in history and the second longest B-2 mission ever flown. It was also the debut combat use of the powerful GBU-57 MOP.
A graphic released by the Pentagon showed the flight path passing over Lebanon, Syria, and Iraq, though it remained unclear if these neighboring countries were notified in advance. Most U.S. lawmakers were also reportedly kept in the dark until shortly before the strike. An anonymous U.S. official confirmed that a woman was among the pilots flying the B-2s on the mission.
Aftermath and Broader Context
Initial satellite imagery appeared to confirm damage at the targeted sites, particularly Fordo. Despite the U.S. claims of devastating success, both Iran’s Atomic Energy Organisation and the U.N.’s International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) reported no immediate signs of increased radiation levels near the facilities following the attack.
The U.S. strike significantly escalated the regional tensions already heightened by Israel’s ongoing campaign against Iranian targets. While U.S. officials stated the mission was not aimed at regime change but rather at compelling negotiation, President Trump later hinted at a desire for a different future for Iran with the phrase “MAKE IRAN GREAT AGAIN.”
The timing and justification for the strike drew scrutiny, particularly after President Trump publicly contradicted his own Director of National Intelligence, who had testified weeks earlier that Iran was “not building a nuclear weapon” and that the Supreme Leader had not authorized a nuclear weapons program since 2003. Critics suggested Trump might be dismissing intelligence assessments for political reasons to justify the military action.
Expert analysis varied, with some questioning the assessment of an imminent threat and warning that attacking a non-nuclear state (Iran maintains its program is peaceful, while Israel is widely believed to possess nuclear weapons) could paradoxically push Iran towards seeking a nuclear deterrent. The attack prompted stern warnings from the UN Secretary-General about the risk of the conflict spiraling out of control and threats from Yemen’s Houthi rebels against U.S. ships.
In the wake of the attack, U.S. Central Command increased force protection measures for American personnel in the region, anticipating potential retaliation from Iran and its proxies. While the U.S. presented Operation Midnight Hammer as a decisive blow delivered with unprecedented stealth, the long-term consequences for the region and Iran’s nuclear ambitions remain uncertain.