hangzhou, China, is rapidly solidifying its position as a major global center for artificial intelligence. This vibrant city, nestled near the picturesque West Lake, has cultivated a dynamic tech ecosystem challenging Silicon Valley’s dominance. Fueled by strategic government backing and the clustering of tech giants like Alibaba and DeepSeek, Hangzhou is attracting a new generation of entrepreneurs and developers. They are converging in areas like the Liangzhu suburb, creating a unique “coder village” where groundbreaking AI ideas take root and flourish, aiming to define the future of technology.
The Rise of Hangzhou as China’s AI Epicenter
Just a decade ago, Hangzhou wasn’t widely recognized on the global tech stage. However, provincial and local governments initiated targeted policies offering significant subsidies and tax incentives for new technology companies. This deliberate strategy has successfully nurtured hundreds of startups, transforming the city into a magnet for innovation. Hangzhou now stands as a pivotal location in China’s ambitious push for AI leadership, drawing talent and investment from across the country and beyond.
The city’s appeal is multifaceted. Beyond government support, Hangzhou offers a lower cost of living, particularly lower rents, compared to established tech hubs like Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen. This makes it an attractive destination for young tech professionals and aspiring founders, many in their 20s and 30s, seeking to launch their ventures. The proximity to major tech powerhouses provides a fertile environment for networking, talent acquisition, and knowledge exchange, creating a potent mix for accelerating AI development.
Government Support and Its Double Edge
Government support has been a cornerstone of Hangzhou’s tech boom. Subsidies and tax breaks have provided essential early-stage funding for numerous startups. This assistance can be invaluable for navigating the initial challenges of building a company. For example, some founders have received direct government help in connecting with early investors, including prominent figures from the tech industry.
However, this reliance on state backing also presents complexities. Several founders report difficulties attracting foreign venture capital. Overseas investors express caution due to concerns about potential ties between Chinese tech companies and the government. This creates a strategic dilemma for startups: accept government funding and potentially limit market focus to China, or pursue more challenging routes for international funding and expansion. Many find the former path the most feasible, tailoring their products primarily for the vast domestic market. The potential for international scrutiny, like that faced by ByteDance (TikTok’s parent company), remains a significant worry for companies aiming for global reach.
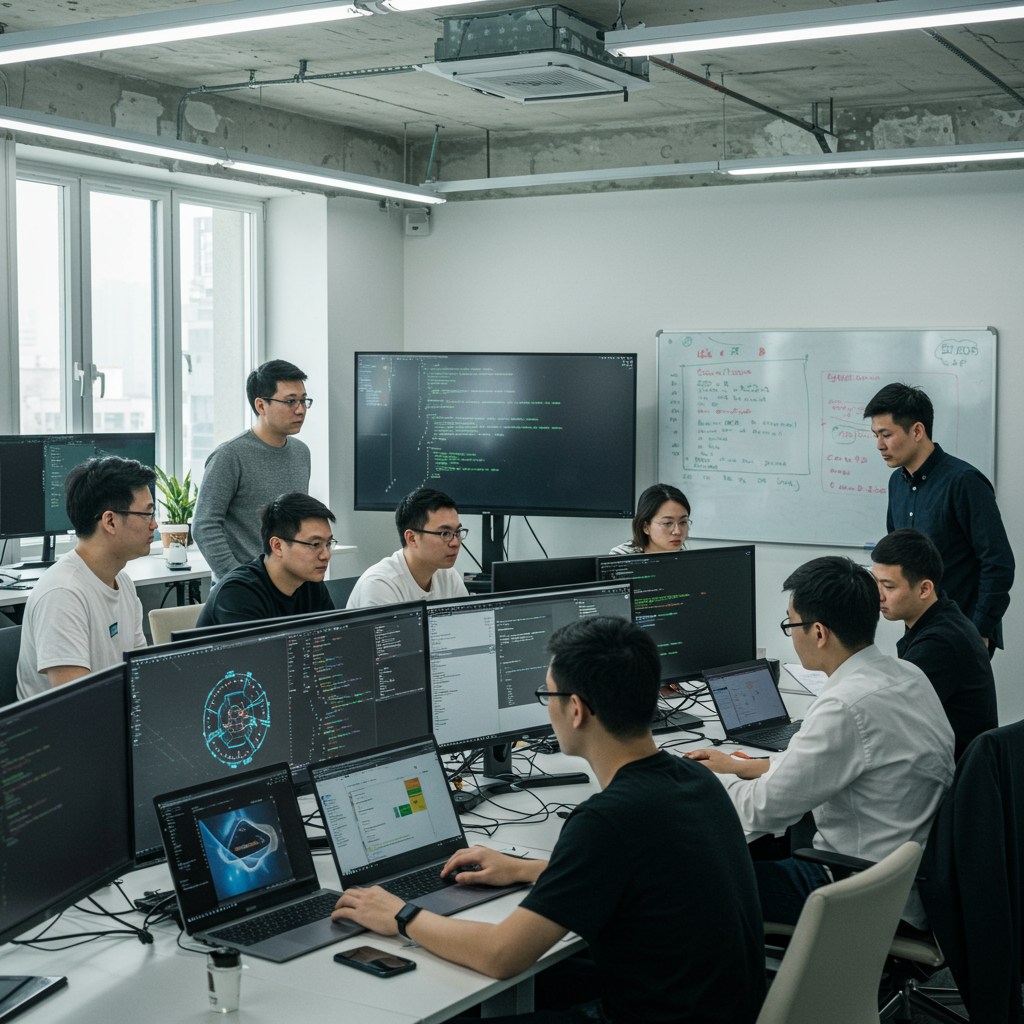
Life in the “Coder Village” of Liangzhu
The suburb of Liangzhu embodies the concentrated energy of Hangzhou’s AI scene. Often dubbed the “coder village,” this area features lower rents and a high density of tech professionals. It’s a place where work and community seamlessly blend. Developers can be found coding in local coffee shops during the day. Evenings often involve group activities, from collaborative gaming sessions to informal networking events.
Individuals like Felix Tao, a veteran from Alibaba and Facebook, play a crucial role in fostering this community. His home has become a central meeting point, hosting events where founders pitch ideas to investors in casual settings, like pitches happening right in the kitchen. The atmosphere is described as buzzing with possibility, attracting people eager to “explore their own possibilities” in the rapidly evolving field of AI. This close-knit environment allows for easy collaboration and feedback, with entrepreneurs leaning on neighbors in coffee shops or living rooms to refine their ideas and products.
Many “villagers” are engineers who previously worked at larger companies like ByteDance. They might be observing non-compete agreements before launching their own startups. This influx of experienced talent, combined with the lower cost of living and supportive community, makes Liangzhu an ideal testing ground for new AI concepts and startups.
Key Players and Breakthroughs Driving Innovation
Hangzhou is not just a city of aspiring startups; it is already home to established tech powerhouses. Giants like Alibaba, NetEase, and Hikvision laid the groundwork for the current ecosystem. More recently, companies like DeepSeek have emerged as significant players. DeepSeek made waves by developing a high-performing AI system at a reported fraction of the cost typically seen in Silicon Valley. Both DeepSeek and Alibaba now contribute to the global AI landscape with open-source models that rank among the world’s best, demonstrating the region’s advanced technical capabilities.
The city is also fostering a new wave of promising startups. Chinese media refer to a group of six prominent AI and robotics firms as the “six tigers of Hangzhou.” These include DeepSeek, Game Science, Unitree, and Rokid. Game Science achieved international success with its video game Black Myth: Wukong. Unitree captured national attention with its robotic performances on state television. Rokid focuses on AI-enabled eyeglasses. Many founders of these successful firms share a background rooted in Hangzhou, often having studied at Zhejiang University or worked at Alibaba, highlighting the interconnectedness of the local talent pool.
Concepts like “agentic AI,” where systems can act autonomously, are popular in Hangzhou. Entrepreneurs are building diverse applications leveraging this capability. Examples include AI-powered digital companions that respond to user moods based on personality data and systems designed to manage aspects of personal and professional life, like sending automated, thoughtful communications. The goal is often to create AI that handles routine tasks, freeing up human users for more creative or meaningful pursuits.
Navigating Critical Challenges: Chips and Global Reach
Despite the vibrant ecosystem, Hangzhou’s AI companies face significant hurdles. One major challenge is access to the advanced semiconductors crucial for training and running sophisticated AI models. U.S. restrictions have limited China’s ability to acquire these high-end chips. While some companies have built stockpiles of chips from manufacturers like Nvidia, the long-term sustainability of this supply is uncertain.
Chinese chip manufacturers like Huawei and SMIC are actively working to develop domestic alternatives. However, matching the capabilities of leading international chipmakers is a complex and time-consuming process. The pace at which China can close this technology gap will significantly impact the growth and competitiveness of its AI industry, including the companies based in Hangzhou.
Another challenge, as mentioned earlier, is securing foreign investment and expanding globally while navigating geopolitical sensitivities. Founders must weigh the benefits of domestic government support against the potential limitations it imposes on international growth. Establishing offices in locations like Singapore is one strategy employed to better pitch to foreign investors, but this requires substantial independent capital.
The Hangzhou Atmosphere: Fueling Creativity and Ambition
Hangzhou’s environment extends beyond just tech infrastructure and investment. Set against the backdrop of the scenic West Lake, a site that has inspired Chinese poets and painters for centuries, the city is said to fuel creativity among its tech residents. The unique blend of natural beauty and intense technological focus creates an inspiring setting for complex problem-solving and innovation.
The community aspect in Liangzhu also fosters a distinct culture. It encourages residents, even those without elite university backgrounds, to pursue unconventional paths. The shared living and working spaces, informal events, and collective discussions build a sense of shared purpose and ambition. Discussions, even about films like “The Matrix,” can spark ideas about breaking free from established systems and forging new paths. This atmosphere cultivates a belief that anyone, regardless of their starting point, has the potential to build the next world-changing tech company. This willingness to explore their own way sets Hangzhou’s aspiring founders apart in a culture where traditional career paths are often favored.
The blend of deliberate government policy, established industry presence, incoming talent, a unique community culture, and a focus on cutting-edge AI concepts positions Hangzhou as a critical engine in China’s drive for technological advancement. Despite navigating challenges related to global investment and chip access, the city’s dynamic ecosystem continues to attract innovators drawn by the promise of low barriers to entry, strong community support, and the exciting possibilities within artificial intelligence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes Hangzhou a unique AI hub in China compared to other cities?
Hangzhou’s uniqueness stems from a confluence of factors. It benefits from significant, targeted government subsidies and tax breaks initiated over a decade ago, fostering a strong startup ecosystem. It hosts major tech giants like Alibaba and DeepSeek, providing talent and infrastructure. Crucially, the suburb of Liangzhu offers lower living costs than Beijing or Shanghai while concentrating tech talent in a “coder village” atmosphere that encourages community and informal collaboration. This blend of government support, established industry, affordability, and vibrant community sets it apart.
Which key companies and institutions are driving AI development in Hangzhou?
Several key players are at the forefront of Hangzhou’s AI scene. Established giants like Alibaba and DeepSeek are major contributors, with DeepSeek particularly noted for its cost-effective, high-performing AI models. Zhejiang University is a vital institution, producing highly sought-after graduates and being the alma mater of key figures like DeepSeek’s founder. Promising startups, often referred to as the “six tigers,” include DeepSeek, Game Science (known for video games), Unitree (robotics), and Rokid (AI eyeglasses). Companies like Mindverse and Zeabur also represent the innovative spirit in areas like agentic AI and development tools.
What are the main challenges facing AI startups and companies in Hangzhou?
Hangzhou’s AI companies face two primary challenges highlighted in the article. Firstly, attracting funding from foreign venture capital firms can be difficult due to concerns about potential ties to the Chinese government, which may limit global expansion ambitions. Secondly, access to advanced computer chips, essential for powerful AI systems, is constrained by international restrictions. While Chinese firms are developing domestic chip production and some companies hold stockpiles, the long-term security and capability of the chip supply remain uncertain, impacting the pace of technological advancement.
—
Hangzhou’s journey to becoming a leading AI hub reflects a strategic blend of government initiatives, the gravitational pull of established tech companies, and the organic growth of a vibrant, community-driven startup culture. Despite navigating complex challenges like securing foreign investment and ensuring access to vital technology like advanced chips, the city continues to attract ambitious talent. The dynamic atmosphere of places like the Liangzhu “coder village,” coupled with the creative backdrop of the West Lake, positions Hangzhou as a key player in the global race to innovate and define the future of artificial intelligence.