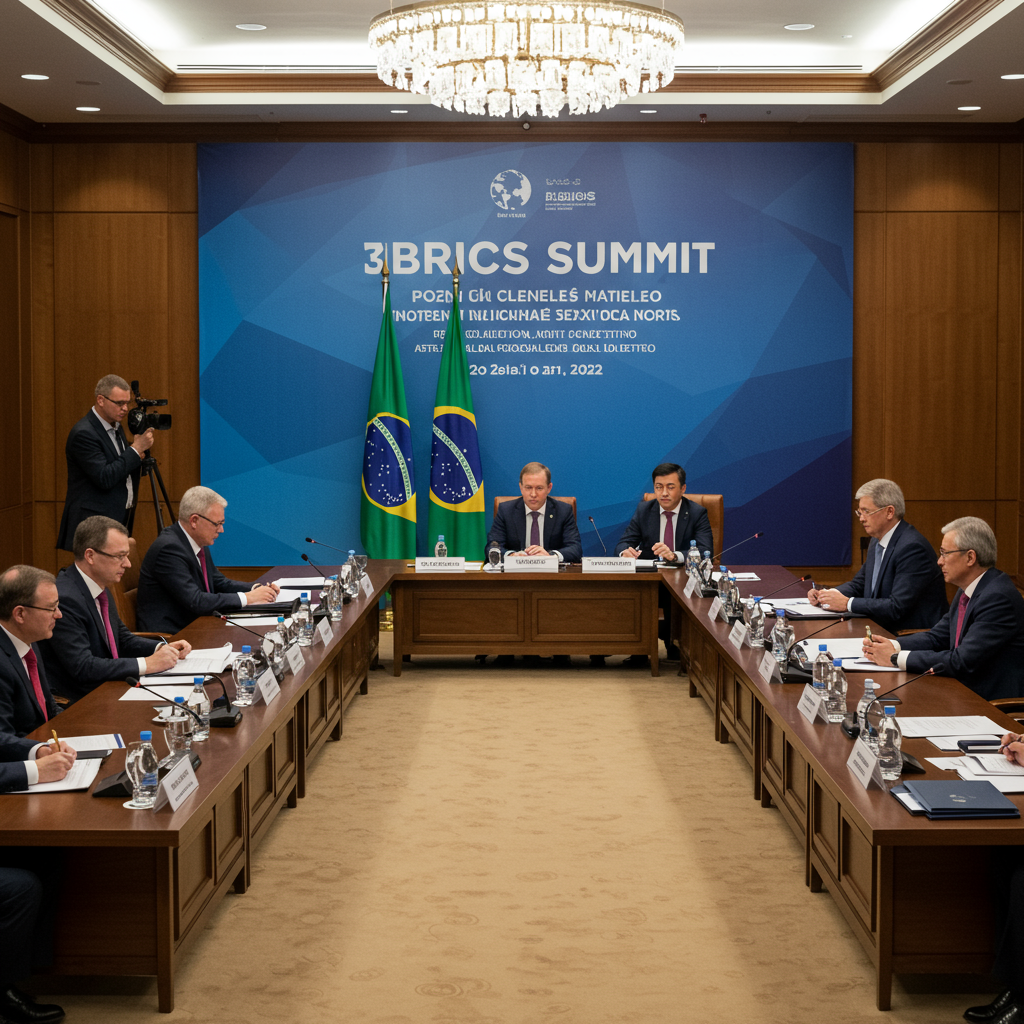
Rio de Janeiro hosted the 17th annual brics summit in July 2025. This high-profile meeting unfolded against a backdrop of significant geopolitical shifts and economic friction. Leaders from the expanding bloc convened to discuss global challenges and chart a path forward. However, the summit proceedings were notably influenced by external pressures. The impact of shifting U.S. tariff policies and escalating tensions in the Middle East loomed large over the discussions.
Emerging economies within the BRICS group voiced strong criticism. Their collective declaration specifically addressed rising tariffs. While refraining from directly naming any country, the statement clearly targeted protectionist measures. The declaration highlighted concerns that these restrictions violate international trade rules. Such policies, the bloc asserted, threaten to slow global commerce. They also risk disrupting complex global supply chains. This introduces significant uncertainty into the international economic system.
Navigating a Complex Global Landscape
The summit took place in Rio de Janeiro. Security forces patrolled iconic locations like Flamengo Beach near Sugarloaf mountain. The setting provided a stark contrast to the intense diplomatic discussions happening indoors. While leaders like Brazilian president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi engaged in talks, two prominent figures were absent. Chinese President Xi Jinping missed a BRICS summit for the first time since 2012. Russian President Vladimir Putin participated remotely via videoconference. Putin’s continued avoidance of international travel stems from an international arrest warrant issued following the 2022 events in Ukraine.
Brazil’s hosting role put President Lula da Silva in a key position. A veteran politician with a background in the labor movement, Lula returned to the presidency in 2023 after a previous term ending in 2011. His political career has seen a shift towards a more pragmatic platform focused on economic growth and social programs, though also marked by significant political challenges and corruption investigations which he consistently denied. As host, Lula sought to steer the conversation. He notably criticized NATO’s plans for increased military spending. He argued that investing in peace is always more difficult than investing in war. This sentiment later appeared in the final BRICS declaration.
Points of Friction and Unanimous Concern
Middle East tensions were another major focal point. The BRICS declaration condemned recent attacks on Iran. However, it stopped short of explicitly naming the United States or Israel. These nations were widely understood to have conducted the strikes in June. Iranian Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi attended the summit. He represented President Masoud Pezeshkian, who was expected to attend before the attacks. Araghchi addressed the BRICS leaders. He urged UN members to strongly condemn Israel. He also called for Israel and the U.S. to be held accountable for alleged rights violations. Araghchi warned of wider damage beyond a single country. He stated the war’s aftermath would impact the entire region and beyond.
Despite the strong condemnation of attacks on Iran, internal differences emerged on other regional issues. BRICS leaders expressed deep concern for the humanitarian situation in Gaza. They collectively called for the release of all hostages. They also urged a return to negotiations. The official declaration reaffirmed commitment to a two-state solution for the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. However, Iran’s representative later issued a separate statement. Via the messaging app Telegram, Araghchi conveyed Iran’s reservation. He noted that the two-state solution “will not work,” citing past failures. In a separate Telegram statement, Russia’s foreign ministry was more direct. It named the U.S. and Israel. The statement condemned the “unprovoked military strikes” against Iran.
The BRICS Stance on Global Conflicts
The conflict in Ukraine received minimal direct attention in the main BRICS declaration. The 31-page document mentioned Ukraine only once. It condemned recent Ukrainian attacks on Russia “in the strongest terms.” The declaration referenced the bloc’s national positions on the conflict. It noted these positions were expressed in relevant international forums. This includes the UN Security Council and the UN General Assembly. This limited mention contrasts sharply with the emphasis placed on other global issues.
Experts offered insights into the summit’s potential and limitations. João Alfredo Nyegray, a professor of international business and geopolitics, commented on the bloc’s struggles for cohesion. He noted that the withdrawal of Egypt’s President and uncertainty surrounding representation from countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE highlighted difficulties. Nyegray suggested this moment required high-level coordination. Instead, he saw signs of dispersion among members. This challenges the BRICS’ aspiration to become a unified pole of global leadership.
Expanding Membership, Shifting Priorities
The BRICS bloc has undergone rapid expansion. Originally comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, it significantly grew last year. New full members now include Indonesia, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and the United Arab Emirates. This expansion brought new dynamics and challenges. The bloc also created a category for “strategic partner countries.” Introduced at the previous year’s summit in Kazan, Russia, this group includes nations like Belarus, Cuba, and Vietnam.
This rapid growth necessitated adjustments for the 2025 summit. Brazil prioritized “institutional development.” This agenda item aimed to better integrate new members. It also sought to boost internal cohesion amidst the enlarged group. Despite some notable absences, the summit remained important for participants. Researcher Bruce Scheidl, from the University of Sao Paulo’s BRICS study group, emphasized this. He noted the instability caused by shifting policies like potential U.S. tariff wars. Scheidl described the summit as a key opportunity for emerging countries. It allows them to seek alternatives and diversify economic partnerships in response to global pressures.
Brazil’s Strategic Balancing Act
Hosting the summit provided Brazil a platform. President Lula advocated for reforming Western-led global institutions. However, Brazil also pursued a careful strategy. The nation aimed to avoid becoming a target for retaliatory measures. Reports indicated concerns about potential U.S. tariffs. Former U.S. President Donald Trump had previously threatened high tariffs against the bloc. These threats were linked to potential moves undermining the U.S. dollar. The previous year’s summit had seen Russia push for alternatives to dollar-dominated payment systems. This move aimed to circumvent Western sanctions.
Brazil’s approach in 2025 seemed more cautious. According to Professor Ana Garcia, Brazil focused on less controversial issues. These included promoting trade relations among members and addressing global health challenges. This strategic choice came after Trump’s return to the White House. Garcia suggested Brazil sought minimal damage. It aimed to avoid drawing negative attention from the Trump administration. This strategy was designed to prevent risks to the Brazilian economy.
Beyond the main agenda, the summit’s host city saw other activities. Protests highlighted diverse global and local issues. A pro-Israel non-profit placed rainbow flags on Ipanema beach. This action protested Iran’s policies regarding LGBT+ people. Separately, human rights group Amnesty International protested Brazil’s environmental plans. Their concern focused on planned offshore oil drilling near the Amazon River mouth. For President Lula, hosting the summit offered a temporary reprieve. It provided a pause from a challenging domestic political situation. Lula faced decreased popularity and conflict with Brazil’s Congress. The meeting also offered a chance to advance climate discussions and commitments. This was particularly relevant ahead of the COP 30 climate talks scheduled for November in the Amazonian city of Belem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were the primary topics addressed at the 2025 BRICS summit in Rio?
The 17th BRICS summit focused on several key areas. Discussions centered on global economic friction, particularly rising tariffs which the bloc condemned as inconsistent with WTO rules. Geopolitical tensions were also prominent, with leaders addressing the situation in the Middle East and, to a lesser extent, the conflict in Ukraine. Brazil, as host, also highlighted institutional development for the expanded bloc, promoting trade relations among members, and global health initiatives.
Which countries were confirmed members of the BRICS bloc at the time of the 2025 summit?
As of the 2025 summit in Rio de Janeiro, the BRICS bloc included its five founding members: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The group had expanded the previous year to add five new full members: Indonesia, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and the United Arab Emirates. This brought the total number of full member states to ten. The summit also noted the existence of a “strategic partner countries” category introduced earlier, including nations like Belarus, Cuba, and and Vietnam.
How did external pressures, like US policies and Middle East conflict, influence the summit?
External pressures significantly influenced the summit’s tone and agenda. The potential for increased US tariffs, particularly under a new administration, led Brazil to adopt a cautious approach, focusing on less controversial topics to avoid economic risk. Middle East tensions, marked by recent attacks on Iran, were a major discussion point, leading to strong condemnations in the final declaration, though sensitive language was used regarding specific actors. These external factors underscored the bloc’s stated goal of seeking alternative economic partnerships and reforming global institutions.
The 2025 BRICS summit in Rio de Janeiro reflected the bloc’s evolving role. Amidst global instability and internal growing pains, the meeting highlighted shared concerns over economic protectionism and regional conflicts. While aspirations for a unified global leadership pole face challenges, the summit provided a vital platform for emerging economies to strategize and seek diversification in an uncertain world.
Word Count Check: 1080 words