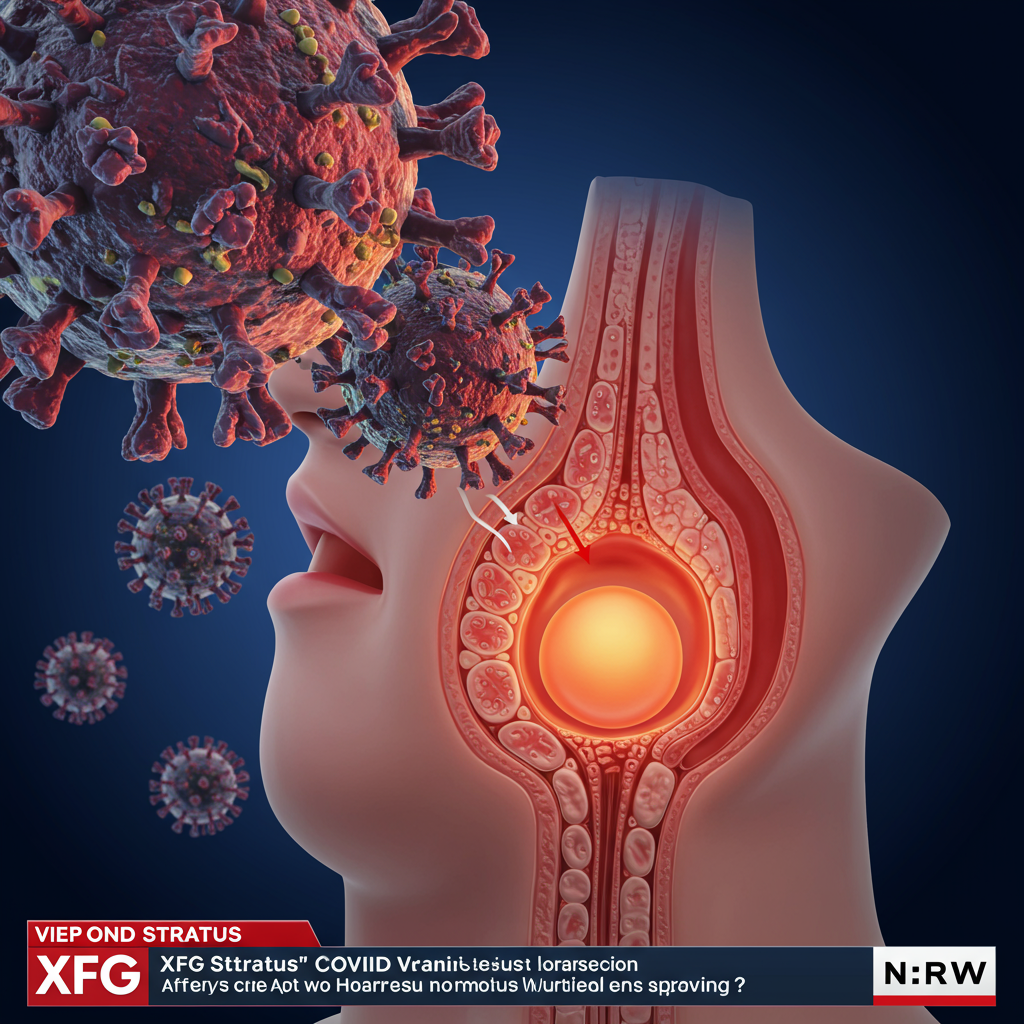
Feeling a tickle in your throat? Is your voice sounding rough or scratchy? While many things can cause hoarseness, this distinct symptom is now linked to a rapidly spreading new version of the coronavirus. Officially known as XFG, but often referred to informally as the “stratus” variant, it has recently been added to the World health Organization’s (WHO) monitoring list due to its increasing global prevalence. Despite its quick spread, public health experts currently assess the risk to be low for the general population. Understanding the signs and staying informed is crucial as new variants emerge.
Understanding the Stratus (XFG) COVID-19 Variant
The constant evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus means new variants regularly appear. Stratus, or XFG, is one such recent arrival now circulating globally. The WHO has classified XFG as a “variant under monitoring.” This designation indicates that the variant has genetic changes that might affect its characteristics and warrants close observation by health authorities worldwide. It helps track its spread, assess its potential impact on public health, and guide future response strategies.
Experts anticipate the Stratus variant will circulate alongside other established variants, like the previously dominant JN.1 and the currently prevalent “Nimbus” variant, particularly throughout the upcoming northern hemisphere summer months. While it’s gaining traction, the WHO’s initial assessment places the public health risk associated with Stratus at a low level based on currently available data. This suggests it doesn’t appear to cause more severe illness overall than other variants in circulation.
The Genetic Makeup of Stratus
Variants like Stratus emerge when the virus replicates and undergoes mutations. The Stratus (XFG) variant is not entirely new in its building blocks; it represents a combination of two existing lineages, LF.7 and LP.8.1.2. This type of recombination can sometimes lead to new properties for the virus.
Scientists analyze specific changes, particularly in the spike protein. The spike protein is critical because it’s what the virus uses to attach to and enter human cells. It’s also the primary target for antibodies generated by previous infection or vaccination. According to the WHO, comparing Stratus to earlier versions like JN.1 reveals “distinct mutational profiles” in this important spike protein. Specifically, mutations have been identified at amino acid positions 478 and 487. These particular changes are believed to “enhance antibody avoidance.” This means the Stratus variant may be more capable of evading immune responses built against earlier strains or through existing vaccines, potentially making reinfection or breakthrough infections more likely.
Tracking Stratus: Global Spread and Data
The Stratus variant first rose to prominence in India. It was reported as the dominant variant circulating there throughout the spring months. From India, the variant began to spread internationally. Tracking initiatives like Gisaid play a vital role in monitoring the global landscape of viral variants. Gisaid is a global science initiative providing open access to genomic data of influenza viruses, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19, and other respiratory pathogens.
Data shared through Gisaid offers crucial insights into how fast and how far new variants travel. In the last week of May, reports from Gisaid indicated a significant increase in the detection of Stratus. At that time, Stratus accounted for 22.7 percent of COVID-19 samples submitted globally for genetic sequencing. This marked a substantial rise from just four weeks earlier, when it made up only 7.4 percent of samples. The samples contributing to this data came from 38 different countries, illustrating that Stratus had achieved a wide geographical distribution in a relatively short period. This rapid increase and international spread were key factors in its designation as a variant under monitoring.
Identifying Stratus: Key Symptoms to Watch For
One of the notable aspects of the Stratus variant highlighted by medical professionals is a specific symptom profile. While many COVID-19 symptoms are common across different variants, doctors in India reported observing a distinctive symptom associated with Stratus infections: hoarseness. This isn’t just a minor throat irritation; it refers to a noticeable change in voice quality, often sounding rough, strained, or weaker than usual.
In addition to this prominent hoarseness, patients diagnosed with the Stratus variant have also frequently reported experiencing a dry cough and a general sore throat. These throat-related symptoms appear to be particularly characteristic of Stratus infections compared to some other variants. Of course, individuals infected with Stratus can also experience the more widely recognized symptoms of COVID-19. These include fever, muscle aches or body pains, and fatigue. If you experience a sudden onset of hoarseness, especially accompanied by other cold or flu-like symptoms, it’s prudent to consider COVID-19 as a possibility and follow local health guidelines regarding testing.
Assessing the Severity and Public Health Risk
A critical question whenever a new variant emerges is whether it causes more severe illness. Based on the available data, the Stratus variant does not appear to be significantly different from other circulating variants in terms of disease severity or mortality rates. Public health experts and the WHO continuously monitor hospitalization rates, ICU admissions, and deaths associated with new variants. Currently, data does not suggest that Stratus leads to a higher incidence of severe outcomes compared to its contemporaries.
The WHO’s assessment that the public health risk posed by Stratus is low is directly tied to this observation. While it spreads efficiently, a variant is considered lower risk if it doesn’t overwhelm healthcare systems by causing a surge in severe cases. It’s important to remember that individual experiences with COVID-19 can vary greatly depending on factors like vaccination status, previous infection, age, and underlying health conditions. However, at a population level, Stratus is not currently flagged as more dangerous than other variants.
Vaccine Effectiveness Against the Stratus Variant
Another major concern with new variants is their potential impact on the effectiveness of existing vaccines. COVID-19 vaccines have been highly effective at preventing severe disease, hospitalization, and death caused by earlier variants. The WHO has addressed the expected effectiveness of currently approved COVID-19 vaccines against the Stratus variant.
According to their risk assessment, current vaccines are expected to remain effective against Stratus, particularly in preventing symptomatic illness and severe disease. This means that while fully vaccinated individuals might still experience breakthrough infections, the vaccines are anticipated to continue offering substantial protection against becoming seriously ill or requiring hospitalization. The WHO emphasizes that it will continue to conduct regular assessments. This ongoing evaluation is crucial for monitoring how effectively vaccines perform against Stratus and other variants as they evolve, guiding decisions on whether updates to vaccine formulations might be needed in the future to maintain optimal protection. Staying up-to-date with recommended vaccinations and boosters remains a key strategy for protecting yourself against severe COVID-19 outcomes.
Living with Evolving Variants
The emergence of variants like Stratus is a natural part of how viruses change over time. The virus causing COVID-19 will likely continue to mutate and produce new versions. The key to managing this ongoing challenge lies in robust global surveillance, rapid data sharing, and public health preparedness. By monitoring variants, understanding their properties (like transmissibility and symptom profiles), and assessing their impact on treatments and vaccines, health authorities can provide timely guidance.
For individuals, remaining aware of circulating variants and their common symptoms, staying current with vaccination recommendations, and practicing good hygiene (like handwashing and covering coughs/sneezes) are effective ways to mitigate risk. If you develop symptoms like persistent hoarseness, consider testing for COVID-19 to confirm the cause and prevent potential spread, especially if you are in contact with vulnerable individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Stratus Covid variant?
The Stratus Covid variant is the informal name for a new version of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, officially designated as XFG. It is a combination of the LF.7 and LP.8.1.2 viral lineages. The World Health Organization (WHO) has added it to its list of “variants under monitoring” due to its increasing spread globally. It was first noted as dominant in India and has since been detected in many other countries.
What are the common symptoms of the Stratus variant?
While Stratus can cause general COVID-19 symptoms like fever, muscle aches, and fatigue, doctors have specifically noted that hoarseness is a common and characteristic symptom of this variant, particularly observed in India. Other frequently reported symptoms associated with Stratus infections include a dry cough and a sore throat.
How effective are current vaccines against the Stratus variant?
Based on current assessments by the WHO, the approved COVID-19 vaccines are expected to remain effective against the Stratus variant. This effectiveness is particularly noted in preventing symptomatic disease and severe outcomes like hospitalization and death. The WHO continues to monitor the situation closely to determine if any updates to vaccine formulations will be necessary in the future.
Conclusion
The Stratus (XFG) variant represents the ongoing evolution of the COVID-19 virus, marked by a unique symptom profile where hoarseness is notably common. While it’s spreading globally and is under close monitoring by the WHO, the public health risk is currently assessed as low, with no indication that it causes more severe illness than previous variants. Crucially, existing vaccines are anticipated to continue offering protection against severe disease. Staying informed about circulating variants, recognizing potential symptoms like hoarseness, and following public health guidance, including staying up-to-date on vaccinations, remains the best approach to navigating the evolving landscape of COVID-19.